Contributors guide¶
DAGMC is an open-source project that facilitates the running of CAD-based particle transport problems.
Contributing¶
Contributing to the DAGMC project is very straightforward. DAGMC is hosted on Github where issues and pull requests are discussed and merged. We use the git version control system, which could be the most unfamiliar aspect of contributing for most people. The general workflow to contribute to DAGMC and many other open source projects involves steps like this:
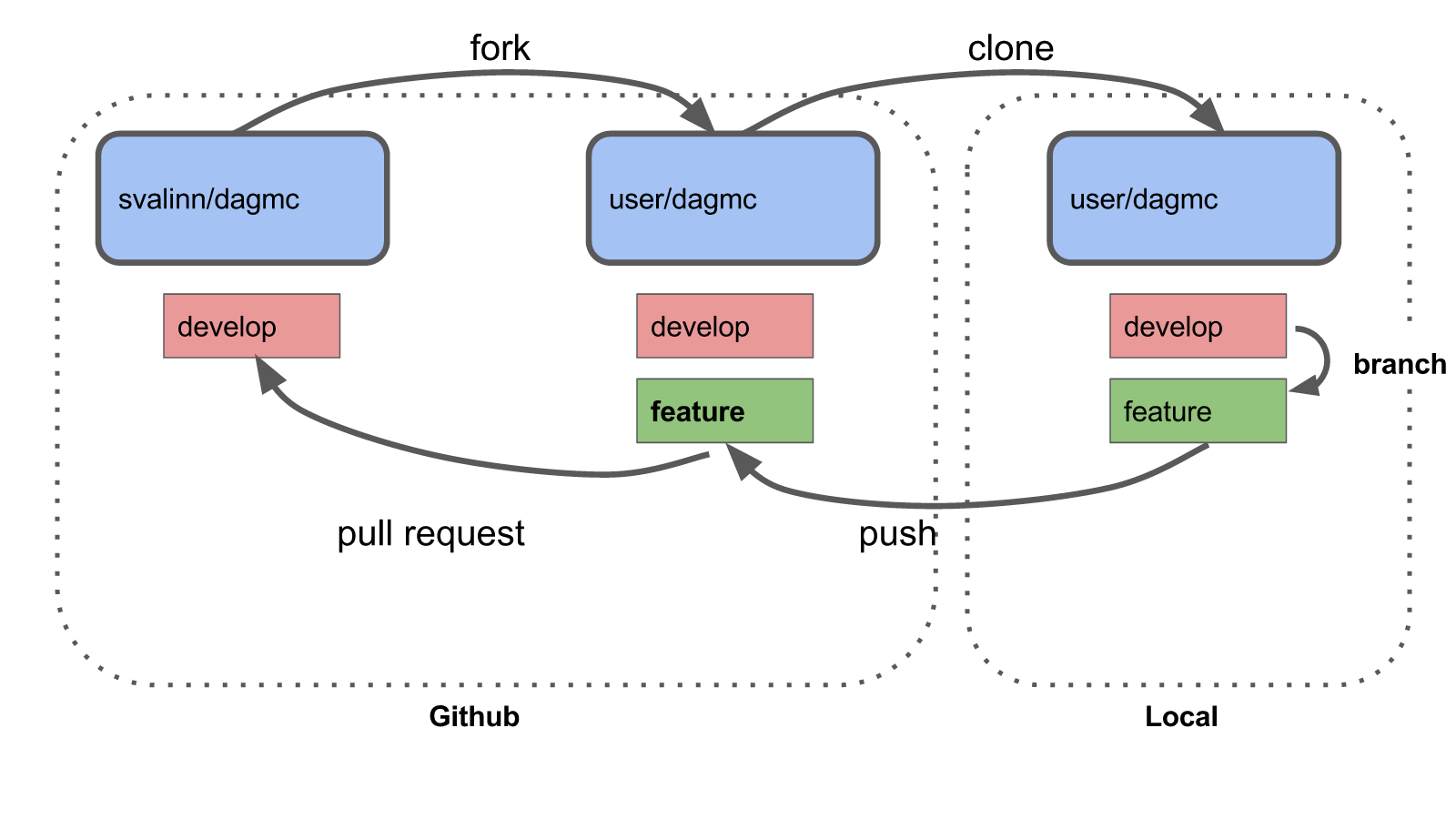
There are 6 main steps:
Forking
Cloning
Branching
Pushing
Pull requesting
Refreshing your branch
These stages are outlined below.
Forking¶
To start, the repository must be forked. The easiest way to do this is to click on the “Fork” button from the svalinn/DAGMC branch shown below.
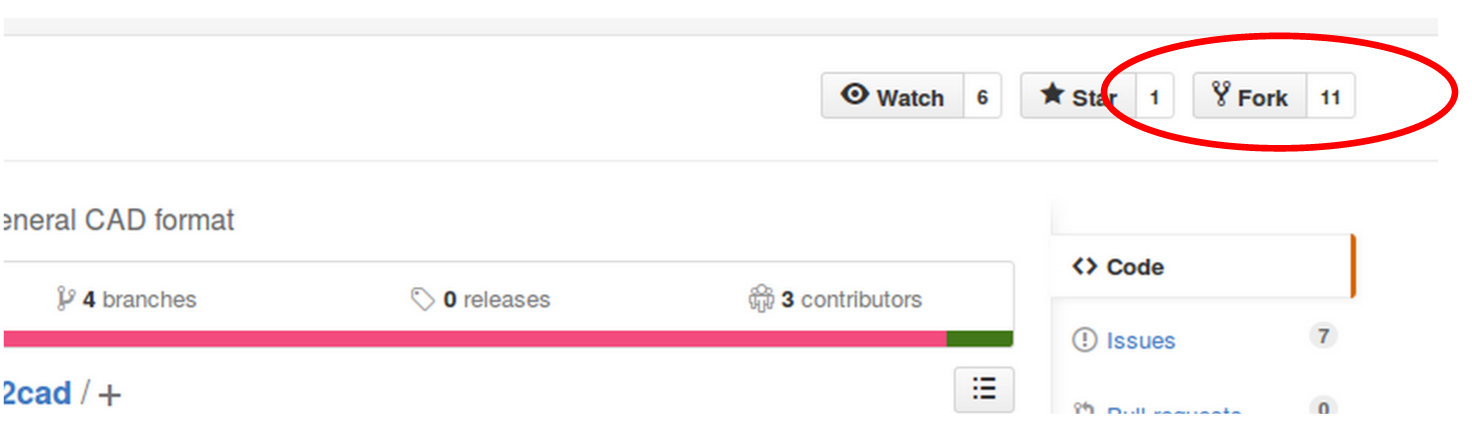
This fork will be an exact snapshot of the svalinn/DAGMC repository at the time you clicked “Fork”. Any new features that you wish to develop should be based from the develop branch of this repository, unless you know exactly what you’re doing.
Cloning¶
You should now clone your fork of this repository to your local machine.
$ git clone https://github.com/<githubusername>/DAGMC
$ cd DAGMC
It is prudent to also add the main svalinn repository as another remote source.
$ git add remote upstream https://github.com/svalinn/DAGMC
Branching¶
The base level of the repository contains folders for each of the supported Monte Carlo codes, the tools directory, and our amalgamated PyNE build. First, you need to checkout a new branch in which to keep your changes.
$ git checkout -b "my_feature_branch"
To insert a new feature, edit an existing file or add new ones as required.
Remember to update the CMakeList.txt files as required. Your new changes
then need to be added, commited, and pushed.
$ git add <files needed to add>
$ git commit -m "This is a message that describes why we need these changes"
Pushing¶
Now that your changes are commited, push the changes to your remote branch in your clone of DAGMC.
$ git push origin my_feature_branch
Before pushing, your local feature branch is the only place this changeset is stored. Pushing is required in order to let your remote repository know of these changes.
Pull requesting¶
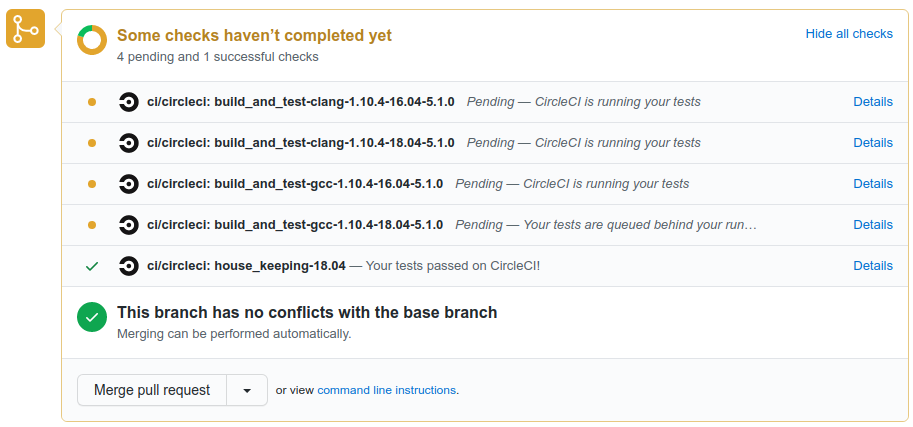
Having succesfully pushed your changes to your remote fork, you can carry on and make more changes, or create a pull request from the changes you have made. If you immediately go to your fork on Github, you should see a message offering to create a pull request with that branch to svalinn/DAGMC:develop. If you click this message you can edit and submit the pull request. If you’ve waited a few tens of minutes between pushing and going to Github, you may need to create a pull request manually. Your pull request will launch our continuous integration tests, and after a short while, your changes will either pass all the tests or fail some of them. The status of the tests is shown at the bottom of the pull request.
All pull requests must be accompanied by a restructured text (.rst) file in the news directory. The file should follow the template in news/TEMPLATE.rst and it should explain the changes made by the pull request in detail.
When testing passes and another developer has reviewed your pull request, your changes will then be merged into the develop branch.
Refreshing your branch¶
Once your pull request has been integrated into the mainline DAGMC develop branch successfully, your clone and your local repository’s develop branch will reflect the pre-pull request state of DAGMC. In order for your personal clones and repositories to be updated, you must first pull the changes into your local clone.
$ git checkout develop #remember to checkout the develop branch!
$ git pull upstream develop
Now your local clone of the repository has an up-to-date develop branch, but you still need to refresh your Github branch, and now you must push the develop changes to it.
$ git push origin develop
Testing and continuous integration¶
We use the Google Test gtest libraries to control testing of our code, and we use the CircleCI continuous integration system to test all changes to the code. When you add features to the codebase, tests should always be added which prove that the capabilities that have been added work.
When a developer makes a pull request on GitHub, CircleCI detects it and launches
the build as specified in the .circleci/config.yml file. CircleCI pulls your feature
branch, the MOAB libraries, HDF5, etc. as required and then launches the tests.
Each test is run in succession and failure is reported if any dependency fails
to build or if any test fails. An example of a CircleCI report is shown below.
Once the testing is complete and your changes have been verified as not breaking any of the existing capabilities, a reviewer will check your pull request over and may suggest some modifications and then will approve or reject your pull request.
General style¶
Explicit namespacing is preferred, so rather than using the using namespace xxx command, you should prefix the variable with the class name. For example,
pyne::Material new_material; // this is a new material
is preferred over
using namepspace pyne;
Material new_material; // this is a new material
This is to save developers poring over dozens of different header files trying to isolate exactly which type is being referenced.
C++ Style¶
DAGMC conforms to the Google C++ style guide. We use the Astyle code formatter to make developers’ lives easier. Here is how to install Astyle on Ubuntu 18.04:
$ sudo apt install astyle
If you are using a distribution of Linux other than Ubuntu 18.04, you may need to acquire astyle manually. This is because DAGMC requires astyle version 3, and not all distributions have easy access to astyle 3. This is the recommended way to get astyle on other versions of Ubuntu, i.e. 16.04:
$ wget https://launchpad.net/ubuntu/+source/astyle/3.1-1ubuntu2/+build/14532685/+files/astyle_3.1-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
$ sudo dpkg -i astyle_3.1-1ubuntu2_amd64.deb
When you have added all the features you want to add, the style guide formatter should be run from the base level directory of the DAGMC repository like this:
$ astyle --options=astyle_google.ini \
--exclude=gtest \
--exclude=src/mcnp/mcnp5 \
--exclude=src/mcnp/mcnp6 \
--ignore-exclude-errors \
--recursive \
--verbose \
--formatted \
"*.cc" "*.cpp" "*.h" "*.hh" "*.hpp"
Then commit the changes to your branch. Avoid commiting code only changes and then commiting C++ formatter changes, as this makes the changeset more difficult to review.
Bug reporting¶
If you find a bug, raise an issue on the main svalinn/DAGMC Github site. If you think you can tackle the issue yourself then please do so, then pull request your changes.